When you build or upgrade a PC, especially for gaming or heavy computing tasks, keeping an eye on your CPU’s temperature is crucial. One of the most frequently asked questions by Ryzen CPU users is whether it’s safe to run the processor at 80°C.
Yes, you can keep your Ryzen CPU at 80 degrees Celsius, but it’s on the higher side of safe operating temperatures. Prolonged exposure to such heat may reduce lifespan, so aim for cooler temps if possible.
To answer this, we need to consider several factors, including performance impact, longevity, and how Ryzen CPUs are designed to handle heat.
What is a Safe Temperature for Ryzen CPUs?
1. Normal Temperature Range:
Typically, Ryzen CPUs are engineered to run safely at temperatures between 35°C to 85°C, with spikes even beyond that during intense workloads. Under idle conditions, most Ryzen CPUs should stay under 50°C, but during gaming or rendering tasks, you might see the temperature climb to 70°C or even higher.
2. Impact of High Temperatures on Performance and Longevity:
Heat is the enemy of electronic components. Sustained high temperatures can degrade your CPU over time, reducing its lifespan and, in some cases, causing performance throttling. However, Ryzen processors come with built-in thermal protection mechanisms to prevent damage.
Is 80°C Safe for Your Ryzen CPU?
1. Manufacturer’s Guidelines for Ryzen CPUs:
According to AMD’s official documentation, Ryzen CPUs are designed to operate safely even at 95°C for short periods. This means that while 80°C is high, it’s still within the acceptable operating range for most Ryzen processors.
2. Factors that Influence Temperature Tolerance:
The tolerance for temperature also depends on your specific workload and whether you’re using overclocking. If you frequently push your CPU to its limits with intense gaming or computing tasks, maintaining lower temperatures can help ensure stable performance and prolong the CPU’s life.
Why Do Ryzen CPUs Run Hot?
1. High Performance Equals High Temperatures:
Ryzen CPUs are built for performance, particularly when dealing with gaming or multi-threaded applications. This high performance naturally generates heat. More cores and higher frequencies create higher thermal output.
2. Overclocking and Thermal Output:
Overclocking pushes the CPU beyond its factory settings, leading to additional heat generation. If you’re overclocking, hitting 80°C becomes more common, but it’s still important to keep an eye on temperatures to avoid thermal throttling.
How to Monitor Ryzen CPU Temperatures:
1. Best Tools for Temperature Monitoring:
There are several tools to monitor CPU temps, including Ryzen Master (AMD’s official software), HWMonitor, and Core Temp. These tools give real-time data on your CPU’s temperature, voltages, and clock speeds.
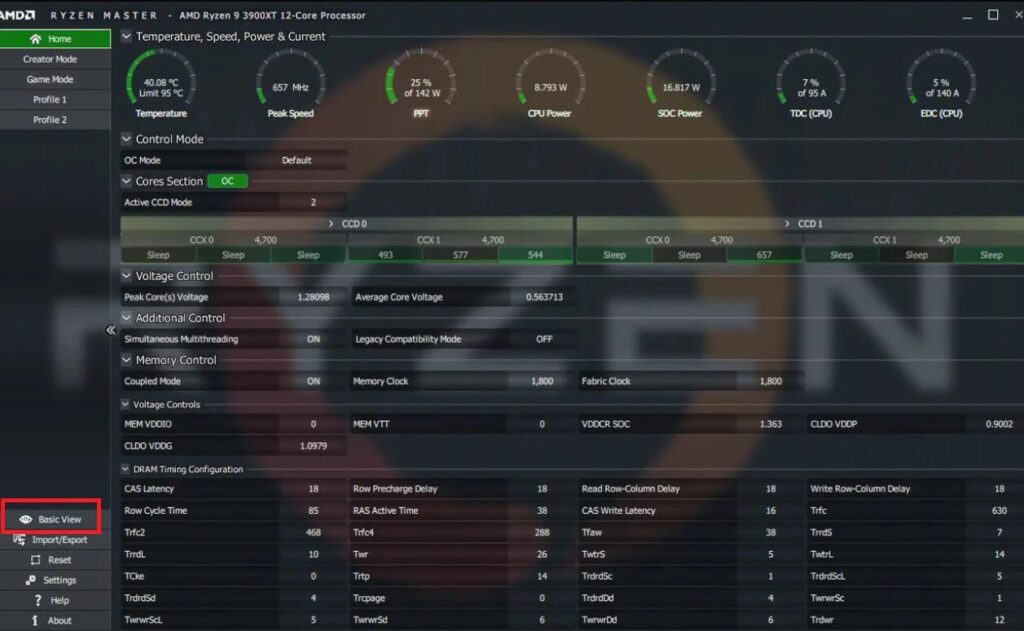
2. Real-Time vs. Idle Temperatures:
Real-time temperatures during demanding tasks will be significantly higher than idle temperatures. Don’t be alarmed if you see your CPU spike to 80°C momentarily during peak workloads.
Ways to Keep Your Ryzen CPU Cool:
1. Improving Case Ventilation:
Good airflow is essential to keep your system cool. Ensure that your case has enough fans and that they are properly positioned to maximize air intake and exhaust.
2. Upgrading to Better CPU Coolers:
If your CPU consistently runs hot, consider upgrading your cooler. Stock coolers often struggle to keep up with overclocked or heavily loaded CPUs.
3. The Importance of Thermal Paste:
Applying high-quality thermal paste correctly can make a significant difference in heat transfer between your CPU and the cooler.
Overclocking and Ryzen CPUs:
1. Balancing Performance and Temperatures:
When overclocking, always balance performance gains with temperature increases. Pushing your CPU too hard can lead to thermal throttling, where the system reduces performance to protect itself.
2. How Overclocking Increases Heat:
By increasing clock speeds and voltages, overclocking forces your CPU to work harder, generating more heat in the process.
3. Should You Overclock If You Hit 80°C?
If you’re hitting 80°C regularly, consider reducing your overclock or improving your cooling solution to avoid long-term damage.
The Role of AVX and CPU Temperature:
1. What is AVX?
AVX (Advanced Vector Extensions) are instruction sets that improve performance for certain tasks but require more power, leading to higher temperatures.
2. How AVX Loads Affect CPU Temps:
When running AVX-heavy workloads, you may notice a temperature spike. Make sure your cooling solution can handle these loads if you regularly use software that relies on AVX instructions.
Does High Temperature Affect CPU Lifespan?
1. How Heat Contributes to Wear and Tear
Extended exposure to high temperatures accelerates the degradation of your CPU. Components can become less efficient over time, potentially leading to failure.
2. Ways to Prolong CPU Lifespan:
Maintaining temperatures below 80°C where possible, using quality cooling solutions, and regularly cleaning your system can help prolong your CPU’s life.
Cooling Solutions for Ryzen CPUs:
1. Air Cooling vs. Liquid Cooling:
Air coolers are effective for most users, but if you’re running demanding workloads or overclocking, liquid cooling can provide better thermal management.
2. Custom Loop vs. All-In-One (AIO) Coolers:
Custom loop cooling systems offer superior cooling performance but are more complex to install and maintain. AIO coolers, on the other hand, are easier to set up and offer great cooling for most users.
Ryzen CPUs and Thermal Throttling:
1. What Happens When Temps Get Too High?
If your CPU temperature exceeds safe limits, the system will throttle performance to protect the processor from damage.
2. How Ryzen CPUs Protect Themselves:
Thermal throttling is an automatic safeguard that prevents overheating by reducing the clock speeds, ensuring that your system remains stable.
Undervolting: A Method to Control Temperature!
1. What is Undervolting?
Undervolting reduces the voltage supplied to your CPU, which decreases heat production without significantly impacting performance.
2. Benefits and Drawbacks of Undervolting:
While undervolting can reduce temperatures, it may also lead to instability if not done carefully. However, many users find it to be a viable solution for lowering temps without sacrificing performance.
Ambient Temperature and Its Impact:
1. How Your Room’s Temperature Affects Your CPU:
The temperature of your environment plays a large role in how your system manages heat. A hotter room means a hotter system, so try to keep your space well-ventilated and cool.
2. Tips for Keeping Your Workspace Cool:
Consider placing your PC in a cooler area, using external fans, or even using air conditioning to maintain an optimal ambient temperature for your components.
Ryzen CPUs in Gaming vs. Productivity:
1. Do Games Cause Higher Temperatures than Other Tasks?
Yes, gaming typically places a heavier load on your CPU compared to regular productivity tasks, resulting in higher temperatures.
2. How CPU Loads Vary Across Different Applications:
Productivity applications like video rendering or 3D modeling can also cause spikes in temperature, but the CPU load tends to be more constant, unlike the peaks and valleys seen in gaming.
Conclusion:
So, is 80°C really that bad for your Ryzen CPU? In short, no—it’s still within a safe operating range, especially for brief periods. However, for the long-term health of your CPU, you may want to explore better cooling solutions, particularly if you’re overclocking or regularly pushing your CPU to its limits.
FAQ’s:
1. What is the ideal temperature range for Ryzen CPUs?
Most Ryzen CPUs operate safely between 35°C and 85°C, with spikes up to 95°C during heavy tasks.
2. Can high temperatures damage my CPU?
Yes, sustained high temperatures can reduce CPU lifespan and lead to performance throttling.
3. Should I invest in liquid cooling?
If you regularly push your CPU to its limits or overclock, liquid cooling can help manage temperatures more effectively than air cooling.
4. How often should I replace thermal paste?
It’s generally recommended to replace thermal paste every 1-2 years, or sooner if you notice temperature spikes.
5. Is undervolting safe for my CPU?
Yes, but it should be done carefully to avoid system instability. It’s a good way to reduce temperatures without sacrificing performance.












